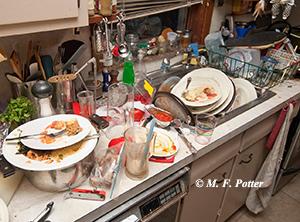Insecticide For Cockroach
Cockroaches are among the most common pests infesting homes and apartments. They are especially troublesome where food is prepared and sanitation is lacking. Cockroaches are repulsive and embarrassing to most people simply by their presence. They may contaminate food, kitchen utensils, and other household items, and they leave an unpleasant odor.
Because cockroaches move freely from filth to food, they can transfer pathogenic microbes that cause food poisoning and other illnesses. Many people are also allergic to cockroach excrement and their shed skins. Cockroach-produced allergens may cause congestion, sneezing and watery eyes, as well as life-threatening bronchial inflammation (asthma) characterized by recurrent cough, wheezing, and difficulty breathing. Asthma triggered by cockroaches is especially common among children living in densely populated housing conditions where infestations are often severe.
Fig. 1: Cockroaches contaminate food and can transmit harmful pathogens.
Cockroaches enter buildings in a variety of ways. The ubiquitous German cockroach is often introduced in infested grocery bags, beverage cartons, or furniture. Species such as the American, Oriental, and wood cockroach also gain entry through gaps around windows, doors, vents, and utility openings, and in firewood. In multi-unit dwellings such as apartments, cockroaches also travel between units through common walls, ceilings, etc. Consequently, while roaches usually thrive where sanitation is poor, even clean homes can become infested.
This publication will help you eliminate your cockroach problem and reduce the risk of future infestation.
Description and Habits
Cockroaches are flattened, brownish, fast-running insects, with long, slender antennae. There are three life stages: egg, nymph, and adult. The female cockroach produces small, brown, bean-shaped egg cases that are deposited in out-of-the-way places. Several nymphs emerge from each egg case (up to 40 with the German cockroach, 15-20 with other varieties). The nymphs resemble adults except that they are smaller and lack wings. The nymphs gradually become larger and inhabit the same places as the adults. Cockroaches are prolific breeders. Species such as the German cockroach are capable of producing several thousand offspring in less than a year.
Cockroaches do not live in centralized nests or colonies like ants, bees, and termites. However, cockroaches do congregate in distinct areas, in response to aggregating odors in their feces. The droppings appear as pepper-like specks in areas of current or former activity. The spotting is similar in appearance to that of bed bugs, but can usually be distinguished by location, or by other signs of infestation. (Cockroaches seldom congregate on beds in the manner of bed bugs.)
Cockroaches are more active at night than during the daytime. During the day, they generally remain hidden in cracks and other dark, secluded areas. At night, they leave their hiding places and search for food. Cockroaches will eat all human foods, plus many other items such as soap, toothpaste, glue, hair, excrement, and filth.
In order to eliminate cockroaches, it helps to know where they are hiding. Preferred locations include warm, dark, moist areas, especially in kitchens and bathrooms. However, depending on the species and extent of infestation, cockroaches may be found anywhere in the home.
Types of Cockroaches
There are 69 species of cockroaches in North America, but only a handful infest structures. Knowing which type of cockroach is present will assist you in knowing how to proceed.
German Cockroach (Blattella germanica) – This is by far the most common cockroach infesting homes and buildings. The pest thrives in the presence of humans but does not occur outdoors. Adults are light brown and about 1/2 inch long, with two dark stripes running lengthwise along the shield-like area behind the head. The nymphs are smaller and darker with a tan stripe down the middle of the back. German cockroaches reproduce very rapidly, which is one reason why controlling these pests can be difficult. A single mated female can produce thousands of new cockroaches in less than a year.
Fig. 2: German cockroaches are common and prolific pests within buildings
(Lower Photo: Gary Alpert, Harvard University, Bugwood.org)
German cockroaches require warmth, moisture, and food, which is why they are most common in kitchens and bathrooms. Preferred hiding places include cracks and crevices under sinks and toilets; beneath/behind refrigerators, dishwashers, and stoves; near trash containers; and inside cabinets and pantries. German cockroaches also congregate in clocks, toaster ovens, and other heat-producing electronic equipment. When populations are large or food is scarce, they can be found in bedrooms, closets, and other areas of the home. German roaches spend most of their time hidden in cracks and crevices, but can be quite mobile. They often travel between rooms or adjoining apartments via walls, ceilings, pipes, wires and other openings.
Fig. 3: Cracks and crevices afford ideal harborage for the German cockroach.
(Photo credit: Tom Myers)
American Cockroach (Periplaneta americana) – This is the largest cockroach commonly found within dwellings, measuring about 1 1/2 inches long when fully grown. It is reddish brown to brown, with a pale yellow band around the edge of the area behind the head. Adults have well-developed wings, but seldom fly. The nymphs are smaller and lack wings, but are otherwise similar in appearance. American cockroaches multiply more slowly than German cockroaches (although the smaller numbers tend to be offset by their size).
Fig. 4: American cockroaches congregate in dark, moist locations.
These cockroaches prefer dark, moist areas, such as in basements and crawl spaces. They often congregate in floor drains, sump pumps, pipe chases, and laundry areas, as well as boiler rooms, steam tunnels, and sewer systems. During warmer months, they can also be found outdoors in yards and around trash containers. American cockroaches often travel long distances from their aggregation sites; long-term relief requires finding and treating these areas.
Oriental Cockroach (Blatta orientalis) – The oriental cockroach is shiny black or dark brown, and the adult is about 1 inch long. The females have very short wings, and the males have wings that cover about half the abdomen. This cockroach typically infests cool, dark, damp places such as sewers, crawlspaces, cellars, and basements. The nymphs and adults are relatively sluggish and usually occur at ground level, often living in floor drains and sump pumps. They also live outdoors under stones, debris, and plant litter, gaining entry into buildings via door thresholds, vents, and other openings. Oriental cockroaches are considered especially filthy because they often feed on garbage, human/animal waste, and decaying organic matter.
Fig. 5: Oriental cockroaches are shiny and black, and often occur in basements and crawlspaces.
(Photo credit: Clemson University – USDA Cooperative Extension Slide Series, Bugwood.org)
Brownbanded Cockroach (Supella longipalpa) – This species is far less common than the German cockroach, but occasionally can be a problem in homes. Correct identification is important because it has markedly different hiding places and habits. The brownbanded cockroach is similar in size to the German cockroach, but lacks the dark lengthwise stripes on the region behind the head. Instead, there is a black bell-shaped pattern behind the head and two transverse yellowish bands across the wings.
Fig. 6: Brownbanded cockroaches look like German cockroaches but often infest different areas.
(Photo credit: Gary Alpert, Harvard University, Bugwood.org)
Brown-banded cockroaches can be found anywhere in the home and are often found in rooms other than kitchens and bathrooms. Preferred locations include upper areas of ceilings, walls, cabinets, and closets; behind picture frames and wall decorations; and beneath or inside furniture. This roach attaches its pea-sized egg capsules to hidden surfaces, such as the undersides of dressers and tables.
Wood Cockroaches (Parcoblatta species) – Although the usual habitat for these cockroaches is outdoors, they often appear in homes, especially in wooded settings. The adults are about 1 inch long and all stages are brownish in color. In some species, the outer wing margin of the adults is edged in white. Unlike the other cockroaches mentioned, male wood cockroaches are excellent fliers, and both sexes are attracted to lights.
Fig. 7: Wood cockroaches live outdoors but often find their way into buildings.
These are primarily outdoor cockroaches, living beneath loose bark in woodpiles, fallen logs, and dead trees. They cannot survive indoors, but can be an annoyance during the spring and summer when large numbers wander in from outside. They are also brought into homes during winter in firewood. Large numbers of woods cockroaches are sometimes found nesting in rain gutters and crawl spaces.
Cockroach Elimination
Cockroaches are best controlled using a combination of techniques. Since roaches flourish where food, moisture, and shelter are readily available, cleanliness is an important step in preventing and correcting problems. Spills and food waste should be cleaned up, and unwashed dishes, utensils, and pet food should not be allowed to sit overnight. Loose food should be stored in tight-fitting containers. Garbage should not be allowed to accumulate, and stacks of paper bags, cartons, and newspapers should be discarded or stored in sealed plastic bags.
Fig. 8: Poor sanitation contributes to cockroach infestations.
Outdoor species such as wood cockroaches can be discouraged from entering buildings by installing tight-fitting screens on windows and sweeps beneath doors. Cracks and openings around doors and windows should be caulked. It is also prudent to seal openings where plumbing pipes or wires pass through walls or floors with caulk, foam, or copper mesh. This is especially useful in apartments to reduce migration of cockroaches between adjoining units.
Fig. 9: Sealing around plumbing pipes helps reduce cockroach movement between apartments.
Insecticide Treatment
Although good housekeeping is helpful, insecticides are usually necessary to eliminate infestations, especially of German cockroaches, which are highly prolific. Cockroaches spend little time out in the open; places that are hard to see and reach is where they tend to be. Dark, secluded areas near food, warmth, and moisture are preferred so a bright flashlight helps when performing inspections. Emphasis should be on finding and treating preferred harborage locations, rather than randomly spraying baseboards, countertops and other exposed surfaces. If key harborage areas are missed problems are likely to continue.
Many types of insecticides are available for controlling cockroaches. Most are sold as liquid or aerosol sprays, while some are formulated as edible baits or dusts. Always read and follow product instructions. This will help you to achieve optimal results while using the product safely. Many insecticides require the removal of food and utensils from treated areas. Removing such items often makes areas more accessible for treatment and prevents possible contamination by the insecticide.
Sprays – When using sprays, target the areas where cockroaches prefer to hide. As mentioned previously, this will vary depending upon the species. Be sure to spray any aggregations or areas with fecal spotting. Avoid spraying walls, floors, baseboards and countertops since cockroaches spend very little time in these areas. (Any roaches that do happen to traverse these areas are unlikely to remain on treated surfaces long enough to absorb a lethal dose.)
Dusts – A few insecticides used for cockroach control are applied as dusts or powders. Most familiar to householders are boric acid and diatomaceous earth. For controlling cockroaches, boric acid tends to be more effective. Roaches succumb to boric acid after crawling over treated surfaces. The tiny particles of powder adhere to the insect’s body, and are ingested as the cockroach preens them from its legs and antennae. Boric acid retains its potency almost indefinitely as long as the dust deposit remains dry.
Insecticide forms of boric acid are sold in bulk cans or a plastic squeeze bottle with a narrow applicator tip. For best results, the dust should be applied as a fine deposit barely visible to the naked eye. Cockroaches tend to avoid heavy accumulations of the powder, much as we would avoid walking through a snowdrift. The easiest way to apply such a small amount is with a ‘bulb’ or ‘bellows’ hand duster sold in hardware stores or online. Key areas to apply boric acid for German cockroaches include crevices along the edges and corners of cabinets; the wall/floor junction behind refrigerator, stove, and dishwasher; and puffed into openings where plumbing from sinks, etc. enter walls. Another potential hiding place for German cockroaches is the void (hollow space) under kitchen and bathroom cabinets. This area can be treated by puffing powder through preexisting cracks at the top of the kick panel. Accessing areas behind dishwashers, stoves, etc., may require removal of the front panel.
Fig. 10: Cockroaches avoid heavy accumulations of boric acid; smaller amounts can be applied with a hand duster.
Never apply boric acid onto countertops or other exposed surfaces, especially those used to prepare food. Traces of powder should be wiped off with a damp cloth. Boric acid should not be injected into electronic equipment as the dust could damage the components.
Baits – Most householders will achieve better results against cockroaches with insecticides formulated as baits. Used correctly, it is possible to achieve results comparable to professional extermination. Cockroach baits contain a slow-acting insecticide combined with a food attractant. Pests find and ingest the bait and crawl away to die. Non-exposed roaches may succumb as well after indirectly ingesting trace amounts of toxicant expelled in the sputum and feces of exposed individuals.
Several excellent cockroach baits are sold in stores and online. Some come in ready-to-use plastic stations (usually 12 to a box), while others come in a large plastic syringe. Popular consumer brands include Combat, Raid, Ortho, and Hotshot. Professional versions of the products sold online include Maxforce, Advion, Advance, Avert and Alpine. Effective ingredients in such products include fipronil, indoxycarb, dinotefuron, abamectin, and hydramethylnon.
Insecticide For Cockroach
An insecticide is a substance or product that acts as a pesticide. In this case, the insecticide we are talking about is a product that kills cockroaches. Cockroaches are one of the most common pests in homes. They can also be dangerous because they can transmit diseases to humans and animals.
Insecticides are often made with synthetic chemicals that have been proven to kill insects such as mosquitoes, fleas and ticks. Some of these chemicals include permethrin and pyrethrin. Insecticides for cockroaches include:
1) Cyfluthrin
2) Bifenthrin
3) Phenothrin
List Of Insecticide For Cockroach
- Advion cockroach bait arena provides complete control of cockroach colinies with the active ingredient indoxacarb.
- The bait’s slow-acting active ingredient provides enough time for cockroaches to transfer it throughout the colony by touching and indirectly through feeding on feces or poisoned carcasses.
- Easy-to-use and long-lasting.
- No residue or odor
Additional Info :
| Item Dimensions | |
| Height | 7.7 Inches |
| Width | 10.45 Inches |
| Length | 6.95 Inches |
- demand cs insecticide offers up to 90 days of control of more than 30 different pests including Ants, cockroaches, mosquitoes, fleas and ticks
- Labeled to control more than 30 pests including Ants, bed bugs, cockroaches, fleas, mosquitoes, scorpions, spiders and ticks
- Cannot be sold in NY
- Country of origin: United States
Additional Info :
| Item Dimensions | |
| Height | 6.05 Inches |
| Width | 3.65 Inches |
| Length | 1.8 Inches |
| Weight | 0.625 Pounds |
- Target pests: Cockroaches
- For use in: Indoors
- Active Ingredient: Abamectin B1 0.05%
- Plunger and applicator tip included
Additional Info :
| Item Dimensions | |
| Height | 1.95 Inches |
| Width | 5.3 Inches |
| Length | 5.55 Inches |
| Weight | 0.4629707502 Pounds |
- Viper EC is for use inside as a crack and crevice spray of nonfood areas including cabinets, windows, doors, closets, shelves, baseboards, and garages. Outdoors Viper may be applied to all areas as a broadcast spray. It has a bit of an odor to it so we recommend testing outside before applying inside.
- Mix Viper Insecticide at a rate of 1.3 oz per gallon of water and apply as a coarse spray to areas of pest infestation. Fill sprayer with the desired volume of water and add Martins Viper EC Insecticide. Close and shake before use in order to ensure proper mixing. Shake or re-agitate sprayer before use if spraying is interrupted. Make up only as required; repeat treatments when needed.
- Ingredients: 25.3% Cypermethrin
Additional Info :
| Color | Dark Amber |
| Item Dimensions | |
| Height | 8.3 Inches |
| Width | 1.5 Inches |
| Length | 6.5 Inches |
| Weight | 1 Pounds |
- Use Cy-Kick when bed bugs, fleas and other hard to eliminate pests are indoors
- Target pests: All types of household and commercial pests including ants, bed bugs, roaches, spiders, earwigs, crickets, centipedes, beetles, and more.
- Broadcast Spray, Crack & Crevice, Spot Treatment
- Cy-Kick is safe to use around children and pets when applied according to the product label
- Use Cy-Kick when bed bugs, fleas and other hard to eliminate pests are indoors
Additional Info :
| Item Dimensions | |
| Height | 1.85 Inches |
| Width | 7 Inches |
| Length | 4.75 Inches |